Top UX Trends 2019
UX design is an ever-changing and evolving craft, with trends coming and going like the change of the seasons. Despite being only halfway through 2019, there are a number of trends that have categorized the first half of the year.
Conversational Design

As a result of technological advancement in AI capabilities, traditional UI web forms will decrease in prevalence. Conversational design integrates many different design disciplines: voice interface design, interaction design, visual and design. All of these various disciplines are used to create a design language which uses elements of human conversation. A conversation is inherently multimodal, and conversation design involves the underlying logic that enables a smooth and coherent dialogue between the user and the system. Furthermore, the conversational design offers that touch of personalization and higher quality user support found in many time-saving designs, double win.
Deep Flat Design
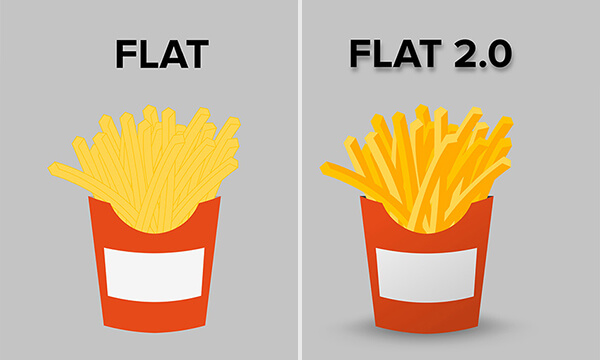
Flat UI has been popular for many years now, and for obvious reasons: it's clean and simple.
Although Flat UI is known for its lack of depth and dimension, this past year has seen a shift towards more depth using pseudo-3D techniques. It entails the stacking of flat layers to create a three-dimensional look and add depth to the elements through shadowing, light positioning, and reflections. As browsers got better, these kinds of features became more affordable and accessible for designers, and complex visual effects have become more and more commonplace within websites.
Motion Design

As computing capabilities consistently increase, we can incorporate more complex visuals and micro-interactions into our UX designs. Motion design refers to animations and other visual effects found in a digital interface used to create a more immersive and meaningful experience for users. When used correctly, motion design can keep users engaged, provide narration, and communicate a brand story. Furthermore, motion design can provide users with guidance and navigation by telling users where to focus and what the next step is to complete their task. If you are considering incorporating motion design into your interface, it's important not to overdo it, as this will frustrate users and clutter their journey with distractions. This would make their task not only more difficult, but more time consuming as well.
Device-Agnostic Design
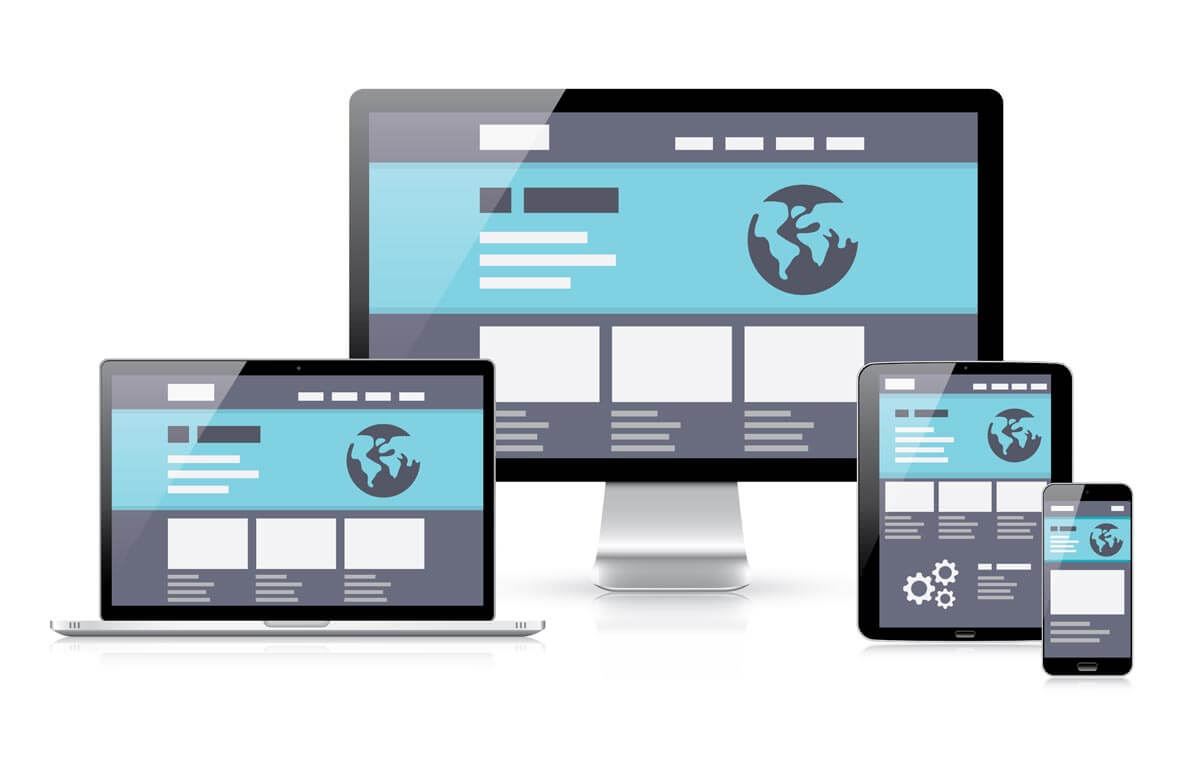

Device agnosticism refers to the compatibility of a software with a variety of different platforms and operating systems, such as a smartphone, a tablet, and even wearable technology. This type of UX design is coming into the spotlight because the number of connected devices people have is rising, and is expected to reach 6.58 per person by the year 2020. As wearables and voice assistants become widespread, apps and websites need to be accessible across various platforms without friction to meet the needs of users. Generally, this type of design takes on a holistic approach that considers the entirety of a users journey rather than focusing on one specific device, interaction, or platform.
Material Design
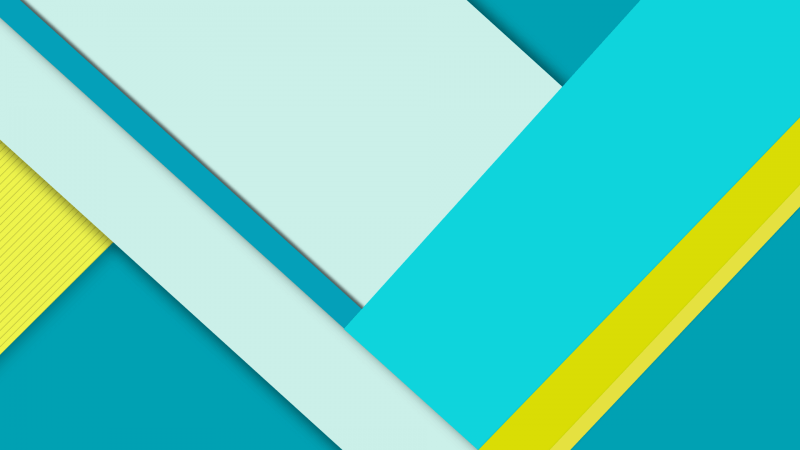
Material design first came about in the android scene several years ago. This design discipline shares many commonalities with flat design, such as the use of minimalism, a variety of colours, and structuredness. However, material UX design also comes equipped with many of its own characteristics such as polgygraphicity, three-dimensionality, interactivity and adaptability to various devices.